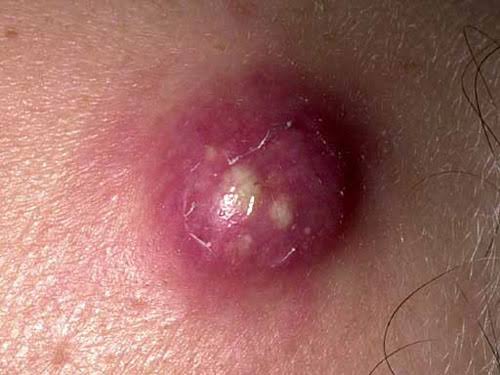
When pus accumulates in hair follicles, skin tissues, or under the skin, a skin abscess occurs. A furuncle is a painful infection, also known as a boil, that forms around a hair follicle and contains pus.
The series of boils that form under the skin is a carbuncle. When hair follicles are infected by bacteria, the follicles can swell and develop into boils and carbuncles.
A furuncle starts as a red lump. Maybe it’s tender. The lump fills with pus quickly, and it can burst as it grows.
Furuncles, boils, and carbuncles usually affect the thighs, armpits, buttocks, face, and neck.
People with compromised immune systems, teens, and young adults are more vulnerable than younger children or older adults to furuncles.
Furuncle or carbuncle?

Furuncles and carbuncles are similar but with some differences.
Skin abscesses that arise from staphylococcal infection are furuncles, or boils. They affect the hair follicles and the tissue around them.
Carbuncles are groups of furuncles under the skin which join together. They impact the layers that are deeper, and they can contribute to scarring.
Symptoms
Both furuncles and carbuncles cause swelling under the skin, and other symptoms can occur, too.
Furuncles
Furuncles develop as pink or red bumps easily. Sometimes, they’re painful. Usually, the underlying skin is red, inflamed and tender.
The lesions almost always appear on the neck, breast, face, buttocks, or thighs. They occur in places that are vulnerable to hair, sweat, and friction, and tend to begin with follicles of hair.
Within a few days, the bump fills up with pus, and it grows. The larger it gets, the more it becomes uncomfortable.
Without any action, furuncles can go away. They often burst and recover within 2 days to 3 weeks without a scar.
Among teenagers and young adults, they are common, and they affect men more than women. Overpopulated and unhygienic living conditions increase the risk.
Carbuncles
A carbuncle, or boil, is less common than a furuncle. It is a collection of boils on one site. It is bigger, reaching up to 4 inches across, than a single boil. Usually, a carbuncle has one or more openings which drain pus onto the skin.
A bacterium known as Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is the most common explanation for a carbuncle. The infection can lead to symptoms of the body that are generalized, including a fever of 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit or higher and a general feeling of unwellness, fatigue, and exhaustion.
The infection can spread to other parts of the body, and it can spread to other people too, so that one can grow at the same time with other members of the household.
On the back, the thighs, or the back of the neck, carbuncles are most likely.
They affect men more often than women, especially older men with poor health or a weakened immune system.
Carbuncle infections appear to be deeper and more serious than those caused by furuncle. The risk of scarring is greater, and it takes longer than furuncles to grow and resolve.
Causes
S. Aureus, also referred to as staph bacteria, is present on the skin and in the nose and throat.
Usually, they are kept under control by the body’s immune system, but often they enter the skin through a hair follicle, or through a cut or graze on the skin.
The immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the affected area to kill the bacteria when the skin becomes infected. Pus is an aggregation of dead bacteria, dead white blood cells, and skin dead.
The following conditions increase the risk of furuncles being developed:
- Diabetes: High levels of blood sugar, or glucose, can reduce the immune system’s ability to respond to infection.
- Medications: Some medications weaken the immune system.
- HIV and some other diseases: Certain conditions weaken the immune systems
- Skin conditions: Psoriasis, eczema, and acne increase susceptibility.
Obesity also increases the risk.
Sometimes, normal bacteria in the nose or on the skin of a person can lead to an abscess. Sometimes, however, when people share room, materials, or devices, such as clothing and whirlpool footbaths, the infection can spread.
Home remedies
The signs of skin abscesses can be relieved by a variety of remedies.
A few times a day, applying a warm face cloth for 10 minutes may help speed up the healing process. In the affected region, heat draws more blood, and thus more white cells, and promotes pore dilation and pus release.
After touching the spot, it is necessary to thoroughly wash your hands and to avoid squeezing a furuncle or carbuncle, as this increases the risk of infection spreading.
Experts advise patients do not attempt to burst furuncles or carbuncles or pinch them. You can see the doctor if the lesion is very painful, if it lasts for more than 2 weeks, or if there is a fever.
Treatment
A sterilized needle may be used by the doctor to lance the abscess, which means pricking it and draining away the pus.

This must not be done at home, but with the appropriate training and supplies by a health care professional.
Only if approved by a medical professional should antibiotics be used.
It may be appropriate to solve hot packs and lancing, but if the infection spreads to a deeper layer under the skin, a medical professional may prescribe antibiotics.
Complications
There is a chance of secondary infection that spreads to other parts of the body as the infection spreads. One kind of potentially extreme secondary infection that may occur is cellulitis.
When to see a doctor
A furuncle normally goes away without treatment after about 2 weeks, but if the abscess is followed by a fever, the person should seek medical aid.
If they have a carbuncle, patients with a chronic condition such as diabetes or cancer or those taking immunosuppressive drugs should consult their doctor.
Prevention
Ways of preventing boils and carbuncles include:
- keeping the skin clean by washing it regularly
- immediately cleansing all skin wounds, cuts, and grazes, however small
- putting a sterile bandage over any cuts to help prevent infection
It will boost your general health and your immune system by eating a healthy, well-balanced diet and having daily physical activity, minimizing the risk of developing furuncles and carbuncles.