Both the Postpill and Postinor-2 are types of emergency contraceptive pills that can be taken to avoid becoming pregnant after engaging in sexual activity without using protection. Find out what makes Postpill and Postinor 2 so similar to one another, as well as their key differences.
After unintended, unprotected sex, it’s common to experience anxiety. The best strategy to avoid pregnancy for those who aren’t ready to start a family is probably to take an emergency contraceptive pill (commonly known as the morning-after pill) right away following unintentional, unprotected sex.
However, some people frequently aren’t sure which birth control pill to utilize because there are numerous varieties available. For instance, there are some parallels and differences between Postpill and Postinor 2, two widely used emergency contraceptives. Many people are unsure of which one to use following unprotected intercourse.
Postinor-2 vs. Postpill will be discussed in this post. We’ll compare and contrast Postpill and Postinor-2 tablets, as well as determine whether one of them is more powerful than the other.
What is Postpill?
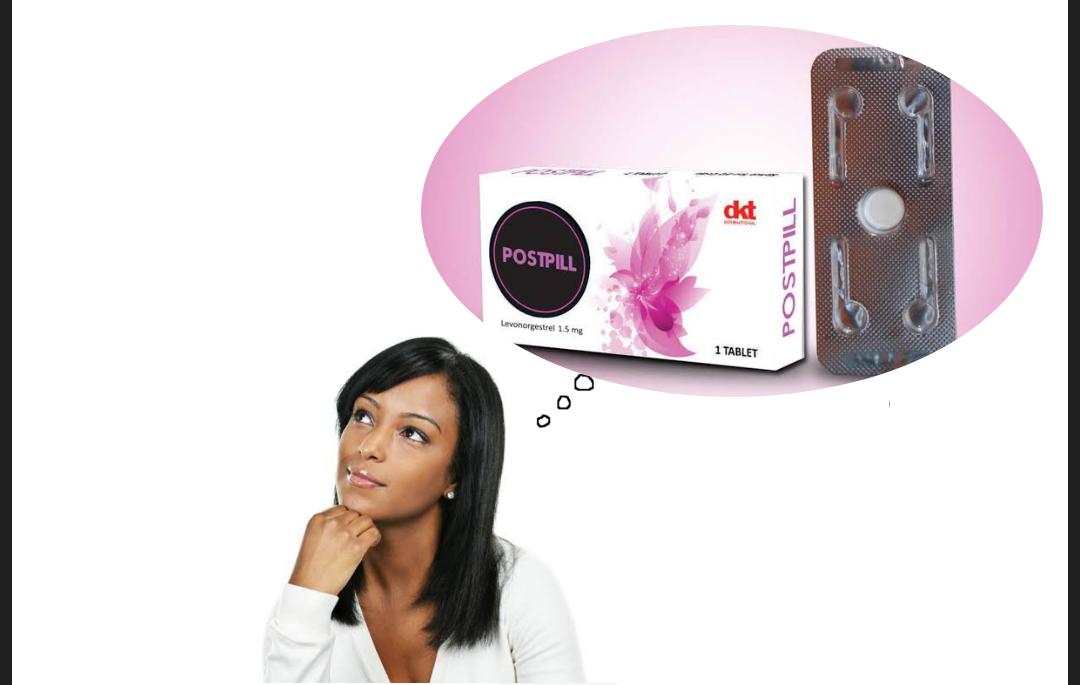

Postpill, often known as the morning-after pill, is an emergency contraceptive pill (ECP). Levonorgestrel, an active component likewise present in conventional birth control pills, is present in high amounts in it.
The company DKT Ethiopia produces Postpill. Only one tablet of the synthetic progesterone levonorgestrel, 1.5 mg, is included in each pack.
ECPs, such as Postpill, are first-line oral medications for the prevention of pregnancy that are FDA- and World Health Organization (WHO)-approved. When taken right after unprotected sex, it helps prevent pregnancy. Even though it functions for up to 72 hours following unprotected intercourse, the earlier you take it, the greater the likelihood that it will stop pregnancy.
By delaying the release of an egg from the ovary, PostPill works (ovulation). Pregnancy cannot occur if you don’t ovulate since there won’t be an egg for the sperm cells released during penetrating intercourse to fertilize. By thickening cervical mucus, which makes it more difficult for sperm cells to pass through and enter the uterus, postpill may help prevent pregnancy.
What is Postinor-2?
Postinor 2 is a “morning after” medication that must be taken within 72 hours of unprotected sexual activity. Postinor 2 is not meant to be used as a regular form of birth control. Levonorgestrel is one type of hormone found in each tablet.
Postinor 2 is predicted to prevent 85% of projected pregnancies. If taken within the first 24 hours of unprotected sexual activity, 95% of predicted pregnancies would be avoided; however, this percentage drops to 58% if taken between 48 and 72 hours later.
Postpill Vs. Postinor-2

There isn’t much of a difference between Postpill and Postinor-2 when compared because both drugs are meant to be used as emergency contraceptives. The number of active components and packaging make Postpill and Postinor-2 different from one another. The differences between Postpill and Postinor-2 are shown in the table below.
| Postpill | Postinor-2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Active ingredient quantity | Contains 1.5 mg levonorgestrel | Contains 0.75 mg of levonorgestrel |
| Pack presentation | A pack contains one pill | A pack contains 2 pills |
| Manufacturer | Manufactured by DKT Ethiopia | Manufactured by Gedeon Richter Plc |
| Usage guideline | The single pill in the pack should be taken immediately after sex or at least within 72 hours | The first pill in the pack should be taken immediately after sex and the second pill taken 12 hours after |
Similarities between Postpill and Postinor-2?
- Levonorgestrel, Postpill, and Postinor-2 all share the same active ingredient, which gives them a lot in common. Postpill and Postinor 2 share a number of similarities, including:
- Each one of them is an emergency contraceptive (also called plan B)
They are both taken orally - Both of these are not meant to be used as conventional birth control pills.
- They both delay ovulation in order to avoid getting pregnant.
- They are both effective when taken immediately after sex or within 72 hours after sexual intercourse
- Neither pill protects against sexually transmitted infections
Postpill Vs. Postinor-2, which is more effective?
Both the Postpill and Postinor-2 are effective at preventing pregnancy if taken shortly after sexual activity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the efficacy of emergency contraceptives like Postpill that are administered in a single dose of 1.5 mg is equivalent to that of those that are administered in two doses of 0.75 mg each.
The use of Postpill and Postinor-2 is likewise not thought to pose any health risks. On the other hand, different people may experience unique adverse effects from using them. It is possible that you will feel okay when using Postpill but that you would suffer adverse effects when taking Postinor-2, but another person may have the opposite experience. It is usually advisable to stick with the birth control option that works best for you rather than experimenting with several methods.
Effects of Postinor-2 and Postpill
Emergency contraceptives like Postpill and Postinor-2 could have some of the same side effects as normal birth control pills. However, the adverse effects are typically not severe and do not persist for an extended period of time.
If you take Postpill or Postinor-2, you can experience some of the following side effects:
- Tiredness
- Breast tenderness
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Mild stomach disturbances
- Changes in the menstruation cycle
Conclusion
Both the Postinor-2 and the postpill are considered to be emergency methods of contraception. They are both effective if taken no more than 72 hours after unprotected sexual activity, despite the fact that they are not intended to be used as a regular means of contraception. It is important that you are aware that neither Postinor-2 nor Postpill will protect you against sexually transmitted diseases.






